In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, one concept has captured the imagination of entrepreneurs, innovators, and industry leaders alike: blockchain technology. This revolutionary innovation has the potential to transform various sectors, disrupt traditional business models, and reshape the way we interact, transact, and trust in the digital age. In this article, “Unleashing the Power of Blockchain Technology,” we will delve deep into the intricacies of blockchain, its underlying principles, applications, and the transformative potential it holds.
Throughout this article, we will navigate the complexities of blockchain technology, shedding light on its potential applications, challenges, and the road ahead. By the end, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the transformative power of blockchain and its implications for various industries, paving the way for a future where decentralized, secure, and transparent systems redefine the digital landscape.
- Chapter 1: The Genesis of Blockchain
- Chapter 2: Blockchain's Impact on Finance and Banking
- Chapter 3: Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
- Chapter 4: Decentralized Applications and Blockchain Platforms
- Chapter 5: Blockchain in Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
- Chapter 6: Blockchain in Identity Management and Digital Privacy
- Chapter 7: Blockchain in the Energy Sector
- Chapter 8: The Future of Blockchain Technology
1. Chapter 1: The Genesis of Blockchain
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and transparent nature, has taken the world by storm. In this chapter, we will explore the origins of blockchain, starting with its connection to Bitcoin and its subsequent evolution into a powerful technology with applications far beyond cryptocurrency.
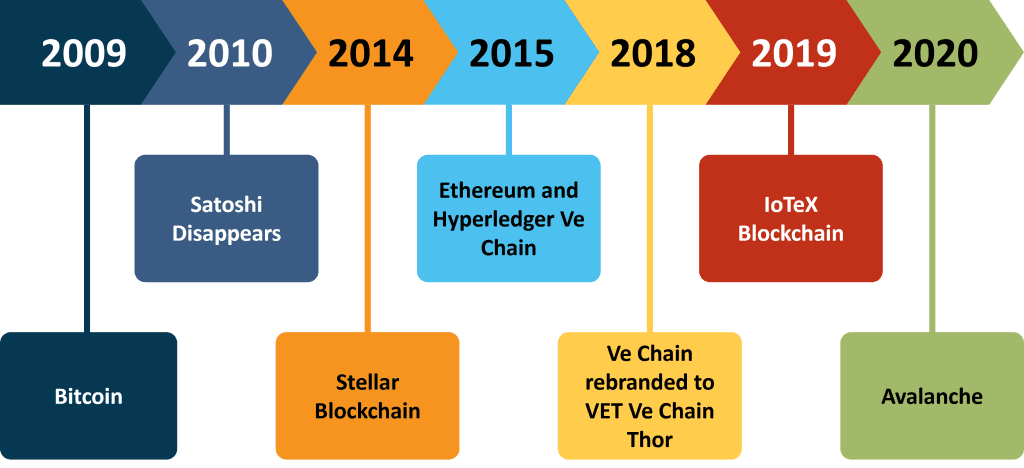
1.1 Exploring the Origins:
From Bitcoin to Beyond The story of blockchain begins with the creation of Bitcoin, the world’s first decentralized digital currency. In 2008, an individual or group of individuals operating under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published the famous Bitcoin whitepaper, outlining the concept of a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. This whitepaper introduced the underlying technology behind Bitcoin: blockchain.
1.2 Understanding Distributed Ledger Technology:
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger, a digital record of transactions that is maintained across multiple computers, known as nodes, on a network. Unlike traditional centralized ledgers, blockchain’s distributed nature ensures transparency, immutability, and security. Each transaction, or block, is linked to the previous one, forming a chain of blocks.
1.3 Cryptography:
The Backbone of Blockchain Cryptography plays a vital role in securing the integrity and privacy of data on the blockchain. Through the use of cryptographic algorithms, transactions and data are encrypted, ensuring that only authorized parties can access and verify them. Techniques such as hashing, digital signatures, and public-private key pairs are used to protect the information stored on the blockchain.
1.4 Consensus Mechanisms:
Securing the Network Maintaining the security and consensus of a decentralized network is a fundamental challenge in blockchain technology. Various consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), have been developed to ensure agreement on the validity of transactions and prevent malicious activities, such as double-spending or tampering with the blockchain.
1.5 Smart Contracts:
Automating Transactions Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules encoded on the blockchain. These contracts automatically execute the terms and conditions agreed upon by the involved parties when certain predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts enable trustless and automated transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing costs.
As we embark on this journey through the genesis of blockchain, it becomes clear that this technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries. From finance and banking to supply chain management, healthcare, identity management, and the Internet of Things, blockchain is disrupting traditional systems and paving the way for innovative solutions.
Stay tuned to uncover the transformative power of blockchain technology and its far-reaching implications for our digital future.
2. Chapter 2: Blockchain’s Impact on Finance and Banking
In this chapter, we will explore how blockchain technology is reshaping the financial and banking sectors. From revolutionizing payments to redefining financial services, blockchain is disrupting traditional systems and opening up new possibilities for efficiency, security, and inclusivity. We will explore how blockchain is revolutionizing payments, redefining financial services through decentralized finance (DeFi), enhancing security and transparency in banking, and opening new possibilities with tokenization and central bank digital currencies.
2.1 Revolutionizing Payments and Remittances:
Traditional payment systems are often slow, costly, and prone to intermediaries. Blockchain technology offers a solution by enabling peer-to-peer transactions with reduced fees and faster settlement times. Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, have emerged as alternative digital currencies that leverage blockchain for seamless cross-border payments and remittances.
2.2 Redefining Financial Services with DeFi:
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is a rapidly growing sector within the blockchain industry. DeFi aims to recreate traditional financial services, such as lending, borrowing, and trading, in a decentralized manner. By leveraging smart contracts and blockchain technology, DeFi platforms provide open and permissionless access to financial services, enabling individuals around the world to participate in global markets.
2.3 Enhancing Security and Transparency in Banking:
The traditional banking system relies on centralized databases, which are vulnerable to hacks and data breaches. Blockchain technology introduces a decentralized approach to storing and managing financial data. By distributing transaction records across a network of nodes, blockchain enhances security and transparency. Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is immutable and can be audited, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing trust in the banking sector.
2.4 Tokenization:
The Future of Asset Management Blockchain enables the tokenization of various assets, including real estate, stocks, bonds, and intellectual property. Tokenization represents ownership rights or assets in the form of digital tokens on the blockchain. This innovation has the potential to democratize access to investments, increase liquidity, and streamline asset management processes, all while ensuring transparency and reducing intermediaries.
2.5 Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and Blockchain :
Several central banks are exploring the potential of issuing Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) utilizing blockchain technology. CBDCs aim to provide a digital form of fiat currency backed by the central bank. By leveraging blockchain’s efficiency and security features, CBDCs can enhance financial inclusion, streamline payment systems, and facilitate cross-border transactions.
As blockchain continues to gain momentum in the finance and banking sectors, traditional institutions are gradually embracing this transformative technology. From enabling frictionless payments to empowering individuals with greater financial autonomy, blockchain is revolutionizing the way we think about and interact with money.
3. Chapter 3: Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
In this chapter, we will explore the profound impact of blockchain technology on supply chain management. From traceability and provenance of goods to streamlining logistics and enhancing sustainability, blockchain is revolutionizing the way we track and manage goods throughout the supply chain.

3.1 Traceability and Provenance of Goods:
One of the key challenges in supply chains is ensuring the authenticity and traceability of products. Blockchain provides an immutable and transparent ledger that can record every stage of a product’s journey. By integrating blockchain with IoT devices, QR codes, or RFID tags, businesses can track and verify the origin, quality, and movement of goods in real-time, reducing the risk of counterfeiting and ensuring compliance with regulations.
3.2 Eliminating Counterfeit Products:
Counterfeit products pose a significant threat to businesses and consumers alike. Blockchain technology offers a solution by creating a tamper-proof record of each product’s history. By scanning a product’s unique identifier, customers can access its blockchain-based record, verifying its authenticity and ensuring they are purchasing genuine products. This transparency helps in building trust between consumers and businesses, fostering brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
3.3 Streamlining Logistics and Inventory Management:
Efficient logistics and inventory management are crucial for supply chain optimization. By leveraging blockchain technology, businesses can streamline processes such as order fulfillment, inventory tracking, and delivery management. Smart contracts on the blockchain can automate tasks like inventory replenishment, payment settlements, and verification of delivery, reducing paperwork, minimizing errors, and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
3.4 Enhancing Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing:
Consumers are increasingly concerned about the ethical sourcing and sustainability of the products they purchase. Blockchain can provide a decentralized and transparent platform to track the origin and journey of raw materials, ensuring compliance with environmental and ethical standards. This transparency empowers consumers to make informed choices, supports responsible sourcing practices, and encourages businesses to adopt sustainable initiatives throughout the supply chain.
3.5 Smart Contracts in Supply Chain Operations:
Smart contracts play a vital role in automating and securing transactions within the supply chain. These self-executing contracts automatically trigger actions based on predefined conditions. For example, a smart contract can release payment to a supplier once the goods are delivered and verified. By eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing manual paperwork, smart contracts increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance trust between supply chain participants.
As blockchain technology continues to mature, its potential in revolutionizing supply chain management becomes increasingly evident. From ensuring product authenticity to improving logistics and promoting sustainability, blockchain is transforming the way we manage and track goods throughout the global supply chain.
4. Chapter 4: Decentralized Applications and Blockchain Platforms
In this chapter, we will explore the world of decentralized applications (DApps) and blockchain platforms. From the foundational platform of Ethereum to other prominent blockchain platforms, we will delve into the innovative applications and possibilities they offer.

4.1 Introduction to Decentralized Applications (DApps):
Decentralized applications, or DApps, are software applications that run on a blockchain network, utilizing its decentralized and transparent features. Unlike traditional applications that rely on centralized servers, DApps leverage the distributed nature of blockchain, providing increased security, immutability, and user control. DApps are revolutionizing various industries, including finance, gaming, social media, and supply chain management.
4.2 Ethereum:
The Foundation of DApp Development Ethereum, the second-largest blockchain platform, introduced the concept of smart contracts, enabling developers to build decentralized applications. With its Turing-complete programming language, Solidity, Ethereum allows for the creation of complex and customizable smart contracts that power DApps. Ethereum’s ecosystem has seen tremendous growth, hosting a wide range of applications, including decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized exchanges.
4.3 Exploring Other Blockchain Platforms:
While Ethereum is a prominent player in the DApp space, several other blockchain platforms offer unique features and capabilities. Platforms like EOS, Cardano, and Tezos provide alternatives for DApp development, each with its own consensus mechanisms, scalability solutions, and programming languages. These platforms aim to address some of the limitations and challenges faced by Ethereum, such as scalability and transaction costs.
4.4 NFTs and their Role in the Digital Economy:
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have gained significant attention in recent years, showcasing the potential of blockchain technology in the realm of digital assets. NFTs represent unique digital items, such as artwork, collectibles, and virtual real estate, with ownership recorded on the blockchain. Blockchain’s immutability and transparency ensure the authenticity and provenance of these digital assets, enabling artists and creators to monetize their work and provide verifiable ownership to buyers.
4.5 Scalability Challenges and Proposed Solutions:
Scalability remains a critical challenge for blockchain platforms, especially when it comes to supporting mass adoption of DApps. As the number of users and transactions increases, the limitations of current blockchain architectures become apparent. Various solutions are being explored, including layer-two solutions like sidechains and off-chain scaling techniques such as state channels and plasma. These scalability solutions aim to improve transaction throughput and reduce fees, making blockchain platforms more efficient and user-friendly.
The world of decentralized applications and blockchain platforms is dynamic and constantly evolving. As developers continue to innovate and improve these technologies, we can expect to see more sophisticated DApps, enhanced scalability, and widespread adoption across various industries.
5. Chapter 5: Blockchain in Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
In this chapter, we will explore the transformative potential of blockchain technology in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries. From enhancing the security and privacy of medical records to enabling efficient drug traceability and fostering decentralized healthcare solutions, blockchain is revolutionizing the way we approach healthcare.

5.1 Securing Medical Records with Blockchain:
The security and privacy of medical records are paramount in healthcare. Blockchain provides a decentralized and tamper-proof system for storing and managing medical data. By utilizing blockchain, sensitive patient information can be securely encrypted, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access and update the records. This transparency and security enable seamless sharing of medical data between healthcare providers, leading to improved diagnosis, treatment, and patient care.
5.2 Efficient Drug Traceability and Authentication:
Counterfeit drugs pose a significant threat to patient safety and public health. Blockchain technology can be utilized to create an immutable and transparent record of each drug’s journey from manufacturing to distribution. With the integration of blockchain, pharmaceutical companies, regulators, and consumers can verify the authenticity and quality of drugs, ensuring that patients receive genuine and safe medications.
5.3 Empowering Patient-Controlled Data Sharing:
In the current healthcare system, patient data is scattered across multiple providers and institutions, making it challenging to access and share vital information. Blockchain enables patients to have control over their health data by storing it in a decentralized and encrypted manner. Patients can grant permission to healthcare providers to access specific parts of their medical records, facilitating more comprehensive and coordinated care while maintaining the privacy and consent of the patients.
5.4 Enabling Interoperability and Data Exchange:
Interoperability, the ability of different healthcare systems to communicate and exchange data seamlessly, is a significant challenge in the industry. Blockchain offers a potential solution by providing a standardized and secure framework for data exchange. With blockchain-based interoperability, healthcare providers, insurers, and other stakeholders can access and share data across different platforms and systems, reducing administrative burdens and improving the overall efficiency of the healthcare ecosystem.
5.5 Decentralized Healthcare Solutions:
Blockchain’s decentralized nature opens up possibilities for innovative healthcare solutions. With the integration of smart contracts, blockchain can enable automated and transparent processes for insurance claims, clinical trials, and supply chain management. Additionally, blockchain-powered telemedicine platforms can facilitate secure and direct communication between patients and healthcare providers, increasing accessibility to healthcare services, especially in underserved areas.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its potential in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries becomes increasingly evident. From securing medical records and ensuring drug authenticity to empowering patients and enabling decentralized healthcare solutions, blockchain is transforming the way we deliver and experience healthcare.
6. Chapter 6: Blockchain in Identity Management and Digital Privacy
In this chapter, we will delve into the implications of blockchain technology in identity management and digital privacy. From the concept of self-sovereign identity to the potential of blockchain in protecting and empowering individuals in the digital realm, we will explore the future of identity on the blockchain.
6.1 Self-Sovereign Identity:
Taking Control of Personal Data Traditional identity systems often rely on centralized authorities to manage and validate personal information. Blockchain introduces the concept of self-sovereign identity, where individuals have complete control over their own digital identities. Through the use of cryptographic techniques, individuals can securely manage and share their personal data, granting selective access to trusted parties while maintaining privacy and control.
6.2 Immutable and Verifiable Digital Credentials:
Blockchain technology provides a reliable and tamper-proof platform for issuing and verifying digital credentials. Whether it’s educational certificates, professional licenses, or government-issued identification, blockchain-based credentials can be securely stored and easily verified by relevant parties. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces the risk of fraud, and streamlines the process of credential verification.
6.3 Enhanced Privacy and Data Protection:
Privacy is a growing concern in the digital age, where personal data is vulnerable to breaches and misuse. Blockchain offers enhanced privacy features through its decentralized and encrypted nature. Personal data stored on the blockchain can be fragmented and encrypted, with individuals holding the private keys to access and control their data. This decentralized approach reduces the risk of data breaches and puts individuals in charge of their own privacy.
6.4 Combating Identity Theft and Fraud:
Identity theft and fraud are persistent challenges in the digital landscape. Blockchain’s transparency and immutability make it difficult for fraudsters to tamper with or forge identities. By leveraging blockchain for identity verification and authentication, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of identity theft, ensuring that individuals are who they claim to be in online transactions and interactions.
6.5 Empowering Digital Inclusion and Accessibility:
Blockchain technology has the potential to empower individuals who lack access to traditional identity systems. Through self-sovereign identity solutions built on blockchain, individuals in underserved populations can create verifiable digital identities, unlocking opportunities for financial services, education, healthcare, and other essential services. This increased accessibility can help bridge the digital divide and foster inclusivity in the digital world.
As blockchain technology advances, its impact on identity management and digital privacy is poised to transform the way we handle personal information. From giving individuals control over their data to improving privacy and combating fraud, blockchain is reshaping the landscape of digital identity.
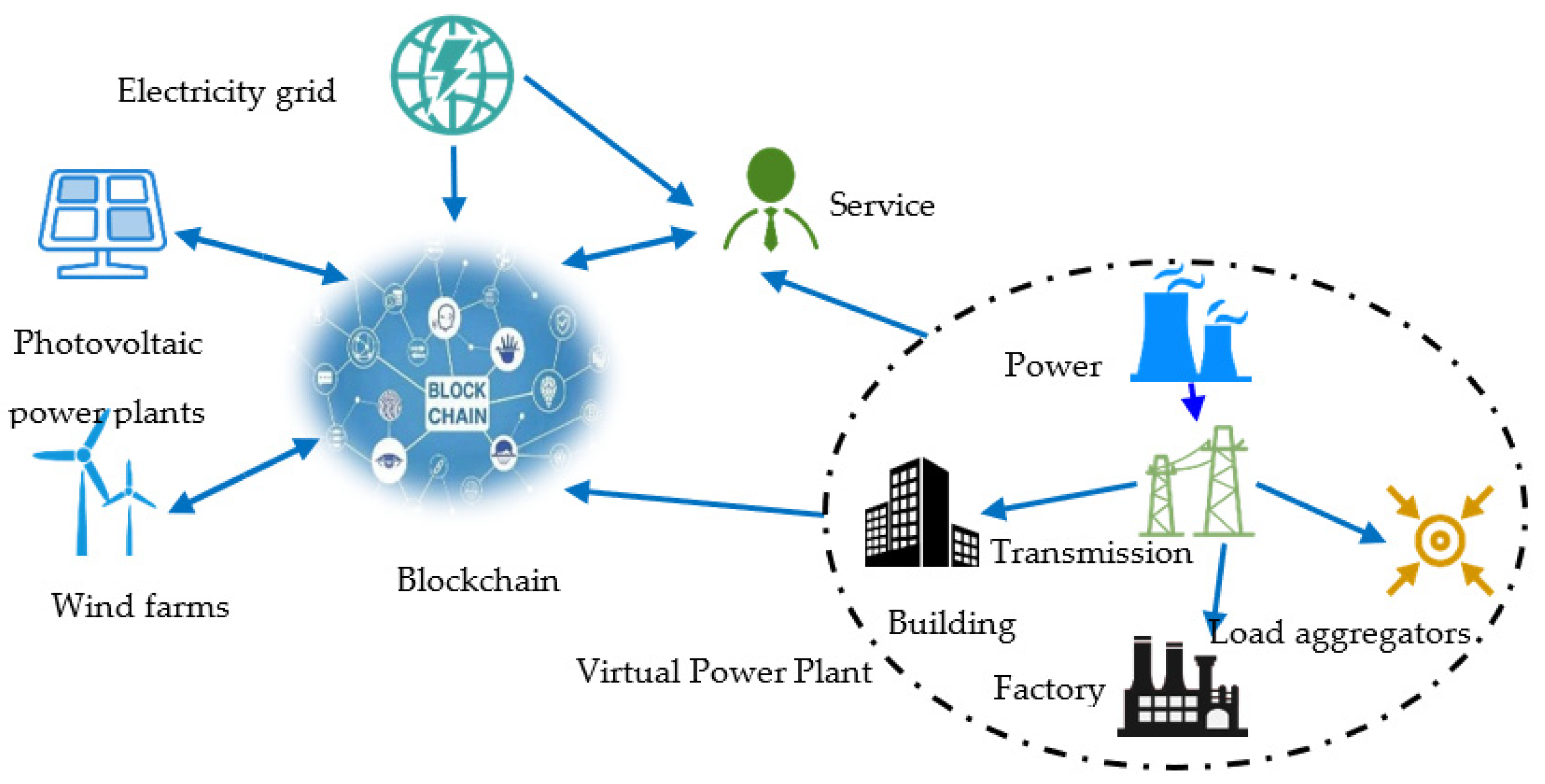
7. Chapter 7: Blockchain in the Energy Sector
In this chapter, we will explore the potential of blockchain technology in the energy sector. From enabling peer-to-peer energy trading to enhancing grid management and facilitating renewable energy initiatives, blockchain is revolutionizing the way we generate, distribute, and consume energy.
7.1 Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading:
Blockchain technology has the potential to disrupt the traditional energy market by enabling peer-to-peer energy trading. With blockchain-based platforms, individuals and businesses can directly trade energy with one another, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction costs. Smart contracts on the blockchain facilitate automated transactions, ensuring transparency, efficiency, and fair pricing for all participants.
7.2 Grid Management and Energy Efficiency:
The integration of blockchain in grid management can enhance the efficiency and reliability of energy distribution. By utilizing decentralized ledger technology, grid operators can track and manage energy production, consumption, and storage in real-time. Smart meters and IoT devices connected to the blockchain enable accurate measurement and verification of energy transactions, allowing for optimized grid management and better energy resource allocation.
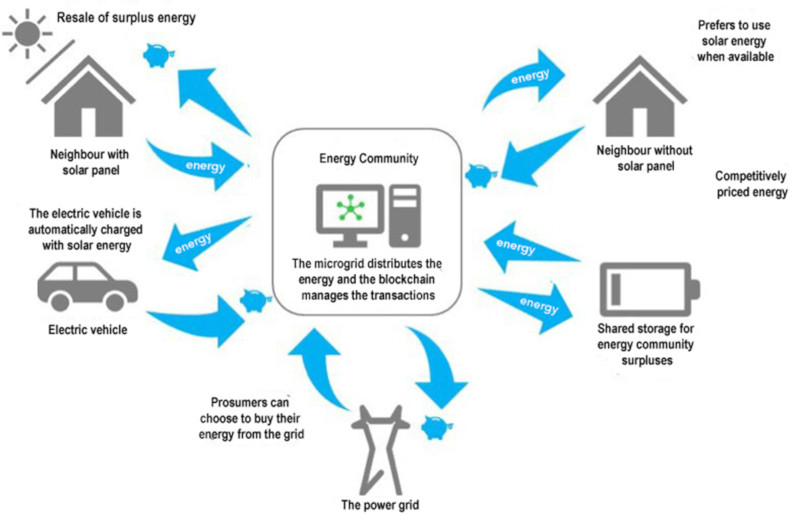
7.3 Renewable Energy Certificates and Tracking:
Blockchain offers a transparent and immutable platform for tracking renewable energy generation and usage. Renewable energy certificates (RECs) can be recorded on the blockchain, providing verifiable proof of clean energy production. This transparency allows consumers to choose and support renewable energy sources, while also enabling regulators and organizations to monitor and incentivize the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
7.4 Microgrids and Energy Resilience:
Blockchain can play a crucial role in the development of microgrids, localized energy systems that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. By integrating blockchain technology, microgrids can enable peer-to-peer energy transactions within a localized community, improving energy resilience, reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure, and promoting energy self-sufficiency.
7.5 Smart Contracts for Energy Management:
Smart contracts on the blockchain provide a secure and automated way to manage energy-related transactions and agreements. For example, smart contracts can facilitate the automatic payment and settlement of energy bills, incentivize energy conservation, or enable demand response programs. These self-executing contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, streamline processes, and increase the efficiency of energy management.
The potential of blockchain technology in the energy sector is vast and transformative. From enabling peer-to-peer energy trading and enhancing grid management to promoting renewable energy initiatives and facilitating energy resilience, blockchain is reshaping the energy landscape towards a more decentralized, efficient, and sustainable future.
8. Chapter 8: The Future of Blockchain Technology
In this final chapter, we will reflect on the key insights gained throughout this book and explore the future prospects of blockchain technology across various industries. As we conclude this journey, we will envision the potential of blockchain in shaping the world in the years to come.
8.1 Blockchain’s Impact on Industries:
Blockchain technology has demonstrated its potential to disrupt and transform multiple industries. From finance and supply chain management to healthcare, identity, and energy, blockchain is revolutionizing how businesses and individuals interact and operate. As the technology continues to mature and scalability challenges are addressed, we can expect to see wider adoption and innovation across industries.
8.2 Interoperability and Integration:
One key aspect for the future of blockchain technology is interoperability. As different blockchain platforms and networks emerge, there is a need for seamless integration and communication between them. Interoperability protocols and standards are being developed to enable the exchange of data and assets across various blockchain ecosystems, fostering collaboration and unlocking new possibilities.
8.3 Integration of AI and IoT with Blockchain:
The integration of blockchain with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) holds tremendous potential. Blockchain can provide a secure and decentralized infrastructure for AI algorithms and IoT devices to interact and share data. This convergence can lead to new applications and business models, ranging from AI-driven smart contracts to autonomous IoT networks secured by blockchain.
8.4 Governance and Regulatory Considerations:
As blockchain technology evolves, governance and regulatory frameworks will play a crucial role in its widespread adoption. Governments and regulatory bodies are actively exploring the development of policies and standards to address concerns around security, privacy, data protection, and compliance. Striking a balance between innovation and regulation will be key to fostering a supportive environment for blockchain technology.
8.5 Scalability and Energy Efficiency:
Scalability and energy efficiency are ongoing challenges for blockchain technology. As more users and transactions enter the ecosystem, scalability solutions like sharding, layer-two protocols, and improved consensus mechanisms are being researched and implemented. Additionally, efforts to enhance the energy efficiency of blockchain networks through consensus algorithms and sustainable mining practices are underway.
8.6 The Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, has emerged as one of the most promising and rapidly growing sectors within the blockchain space. DeFi protocols enable peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and trading without the need for intermediaries. As DeFi continues to gain traction, we can expect to see innovative financial products, improved user experiences, and increased accessibility to financial services for individuals globally.
8.7 NFTs and Digital Asset Ownership:
The rise of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has brought attention to the concept of digital asset ownership and the potential for blockchain to revolutionize the art, entertainment, and gaming industries. NFTs have opened up new avenues for creators to monetize their digital works and provide verifiable ownership to buyers. As the NFT space evolves, we can anticipate further exploration and innovation in the realm of digital assets.
In conclusion, blockchain technology has the potential to transform industries, enhance security and privacy, and empower individuals in the digital era. As we look ahead, it is clear that blockchain will continue to evolve, adapt, and find new applications in areas we may not even imagine today. By embracing the opportunities and addressing the challenges, we can shape a future where blockchain plays a fundamental role in creating a more transparent, decentralized, and inclusive world.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the world of blockchain technology. May your exploration of this groundbreaking technology continue, and may you contribute to its growth and positive impact in the years to come.














+The+Future+of+Technology.jpg)

Wow! Finally I got a website from where I be able to genuinely take valuable information regarding my study and knowledge.
Keep following for more informative contents…